In our hyper-connected world, the humble data cable is the silent workhorse that powers our digital lives. From transferring files between devices to charging smartphones and powering gadgets, data cables are essential for seamless communication and connectivity.
What is a Data Cable?
What is a Data Cable?
A data cable is a physical medium that transfers data between two or more devices. These cables are typically designed with specific connectors to suit different devices and may also carry electrical power in addition to data. Whether it’s charging your phone or syncing data from a digital camera to your computer, data cables bridge the gap between devices.
The Core Functions of Data Cables
The Core Functions of Data Cables
Data cables serve multiple functions, including:
Data Transfer: Enables the transmission of digital information such as documents, images, videos, and more.
Power Delivery: Many cables support power delivery to charge electronic devices.
Signal Transmission: Some cables are designed for transmitting audio and video signals.
Networking: Used to establish wired internet or local network connections.
Common Types of Data Cables
Common Types of Data Cables
Let’s take a closer look at the most widely used data cables:
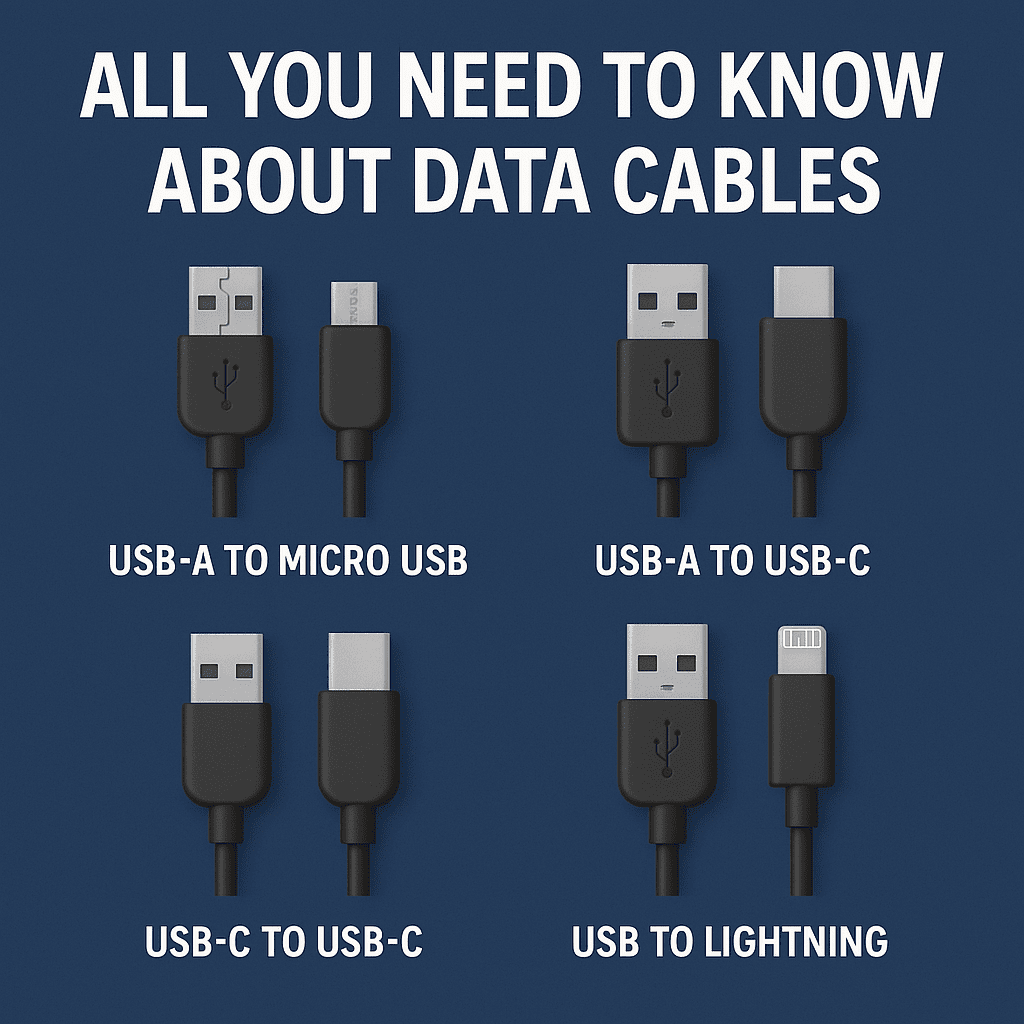
1. USB Cables (Universal Serial Bus)
USB-A to USB-B: Often used to connect printers and other large peripherals.
USB-A to Micro-USB: Used in older smartphones, tablets, and devices like Bluetooth speakers.
USB-A to USB-C: Found in modern devices, offering faster charging and higher data transfer speeds.
USB-C to USB-C: Supports Power Delivery (PD), Thunderbolt 3/4, and ultra-fast file transfer.
Mini USB: Found in older digital cameras and portable drives.
2. Lightning Cable
2. Lightning Cable
Developed by Apple, this 8-pin cable is used for iPhones, iPads, and other Apple gadgets. It supports fast charging and reliable data syncing.
3. HDMI Cable (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
3. HDMI Cable (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
HDMI Cable used to transmit high-definition audio and video from one device to another—commonly between PCs, TVs, monitors, and game consoles.
Standard HDMI
Mini HDMI (for cameras and tablets)
Micro HDMI (smaller portable devices)
4. Ethernet Cable (LAN Cable)
4. Ethernet Cable (LAN Cable)
These cables are essential for wired internet connections and networking.
Cat5e: Suitable for basic home networking.
Cat6 / Cat6a: Offers better speed and less crosstalk.
Cat7 / Cat8: Used in high-speed enterprise networks.
5. SATA Cable (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment)
5. SATA Cable (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment)
Found inside computers to connect hard drives, SSDs, and optical drives to the motherboard.
6. Thunderbolt Cable
6. Thunderbolt Cable
Developed by Intel and Apple, these cables support ultra-fast data transfer, video output, and power delivery through a single connection. Most Thunderbolt cables now use USB-C connectors.
Key Factors to Consider When Buying Data Cables
Key Factors to Consider When Buying Data Cables
With a wide variety of cables available, here’s what you should keep in mind:
1. Compatibility
Ensure the cable is compatible with your device's port (USB-C, Lightning, Micro-USB, etc.). Using the wrong type may result in slow charging or no data transfer.
2. Data Transfer Speed
USB 2.0: Up to 480 Mbps
USB 3.0: Up to 5 Gbps
USB 3.1/3.2: Up to 10–20 Gbps
Thunderbolt 3/4: Up to 40 Gbps
Choose according to your file size and usage needs.
3. Power Delivery
If you're using the cable for charging, check if it supports Fast Charging, Quick Charge, or USB PD (Power Delivery) standards.
4. Durability
Opt for braided cables or those with reinforced connectors to resist fraying and bending. A good cable should last through thousands of plug-unplug cycles.
5. Cable Length
Longer cables are convenient but may reduce power delivery and transfer speed if poorly made.
Applications of Data Cables in Daily Life
Applications of Data Cables in Daily Life
Mobile Charging and Syncing: Smartphones, tablets, smartwatches.
Peripheral Connectivity: Printers, keyboards, mice, external hard drives.
Multimedia Transmission: Connecting PCs to monitors, projectors, TVs via HDMI or DisplayPort.
Networking: Wired internet connection using Ethernet cables for stable and fast connectivity.
Internal PC Connections: SATA and power cables connect hard drives, SSDs, and other components.
Tips for Maintaining Your Data Cables
- Avoid Bending at sharp angles—use cable organizers.
- Store Properly by loosely coiling them when not in use.
- Avoid Overstretching, especially with long-distance connections.
- Keep Away from Heat and water to prevent damage.
Final Thoughts
In a digital-first age, data cables are more than just wires—they’re vital links that keep our devices powered, connected, and productive. Whether you’re a casual user or a tech enthusiast, understanding different types of data cables helps you make informed choices for optimal performance.
From USB to HDMI, Lightning to Thunderbolt, each cable type serves a unique purpose. Always consider compatibility, speed, durability, and intended use before making a purchase. A reliable data cable is an investment in smooth connectivity.